
Testing Equipment
Data Acquistion

DI-1100 Specifications
- 4-Channel Differential Input
- 12 Bit Resolution
- Measure 10 volts (plus or minus)
- Two Digital Inputs
- Includes WinDaq Software
- 20 to 40 kHz sample rate per channel
The best part is the price for the DATAQ DI-1100 including the software is only $59. You can order this unit by going directly to the DATAQ web site.
DATAQ Module DI-1100
The load cells and pressure transducers output a voltage in direct proportion to pressure or force. You will need a Data Acquisition Module to take these voltages and translate them into force and pressure plus store the information. DATAQ manufactures a simple unit (DI-1100) that plugs into the USB port of your desktop or laptop computer. It does not require any external power supply. You simple plug the unit into the USB port of your computer and hook the output wires from the transducer and load cell to the input terminals of the DATAQ DI-1100 unit. Along with the DI-1100 unit comes the USB cable and a powerhouse software program that will graphically display the data in real time on your computer in the right engineering units. It will store the data on your disk and you can export it into various formats included EXCEL.
Transducers
Pressure
Pressure transducers can now be found by doing a Google search. You want to buy a new, good quality one that will stand up to abuse and the harsh environment of solid rocket motor testin. Don’t buy pressure transducers with plastic wetted parts. The plastic parts will melt from the heat of the combustion gases. Make sure the wetted parts on the transducer are stainless steel.
The pressure transducers come in a variety of pressure ranges, but the range most useful to the amateur will be 0 – 1000 psi. If you are making PVC pipe motors, than get the 0 – 500 psi range transducer. If you are only going to buy one pressure transducer, then buy a 0 to 1000 psi. With a 0 to 1000 psi range, you will have all typical chamber pressures covered on your test stand.
It is also good to buy a transducer that has 0.5 volt output at zero pressure. This way you will know the transducer is working before the test. If you get zero volts at zero pressure, you know something is wrong such as a broken wire or the transducer is not working.
Load (Force or Thrust)
Load cells are used to measure the thrust or force generated by the rocket engine during a static test. There a variety of different load cells types, but two main types are cantilever beam and S. Either type can be used easily on a test stand.
Unlike pressure transducers, most load cells do not have a built-in amplifier so the output at maximum force will be in millivolts. This is too low of a voltage to be transmitted any distance. You will need to amplify the signal at the load cell to several volts in order to transmit it to you data acquistion module.
You can buy an amplifier or make your own, which is what we recommend. It is a simple to make one as all you need is a computer chip and resistor. Information on making one is found below.
Load Cell Amplifier
You can make a simple amplifier to boost the voltage output for use in the data acquistion module. A schematic diagram is shown below using an INA-125 chip. You can buy these chips from a number of online sources such as Newark Electronics for about $7 per chip in low quantities.
Even if you have never made electronic components before you can make this one as it consists of only a chip, a chip socket and a resistor. You just solder wires to the connectors on the pin socket and hook it up as shown in the diagram below. The chip pin numbers are shown in the schematic. If you right click on the schematic diagram with your mouse, you can save the schematic on your computer in a larger image format for better viewing. After right clicking on the image, select the “save picture as” option.
We recommend mounting the chip socket on a small board and mounting the board inside a plastic box. You can route the wires to terminal strips outside the box with the connections labeled for easy connection at the test stand. Make the box big enough so you can easily get your fingers inside to insert the chip and replace it with a new one when necessary. Our chips last a couple years sitting in the test stand in Wyoming’s harsh winter environment.
If you use a 9 volt battery to power the chip, the voltage output for the load cell will be 5 volts. If you power it with a 12 volt battery, you will get a 10 volt output. The 10 volt output is better as it will give you more sensitivity.
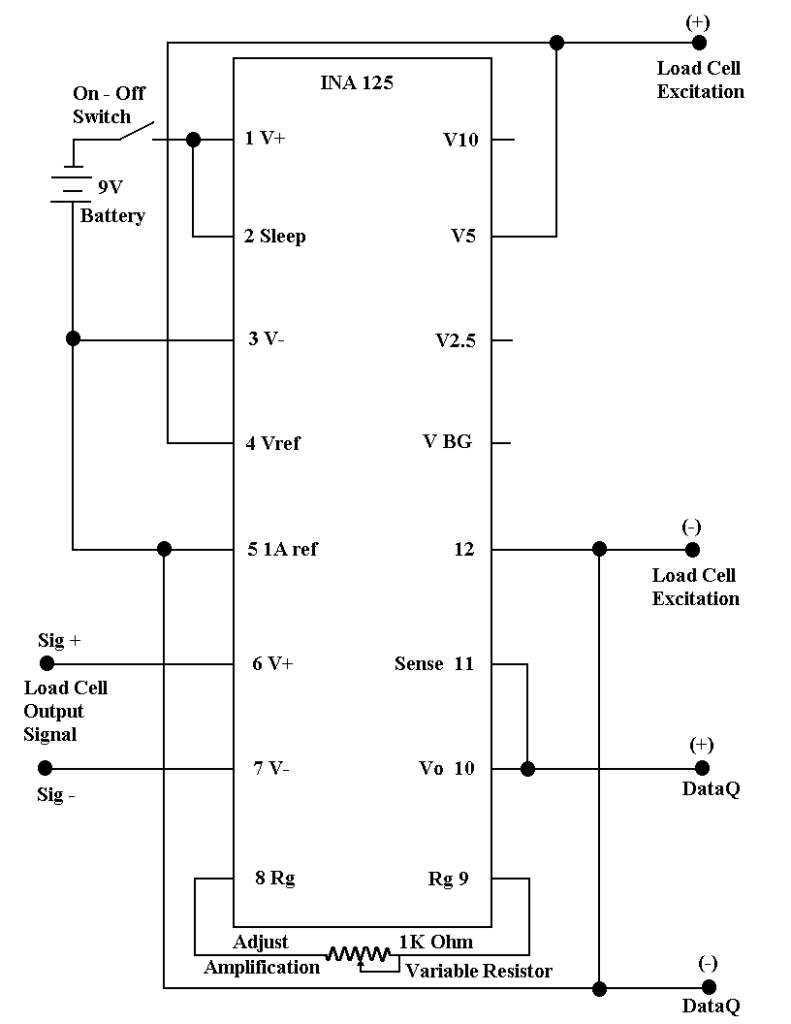
The resistor shown in the schematic is shown as a variable resistor. We actually recommend that you make it a fixed resistor based on the amplification requirements for your load cell and data acquisition system. Variable resistors can shift their position due to handling and vibration causing your recorded values to be off. You should use a high precision resistor with a tolerance of 1%. The value for the resistor can be best illustrated with the following example.
Example: You want a 0 to 6 volts output for the range of your load cell. Your load cell specifications are a rated output of 3 millivolts/volt excitation with a full scale load of 200 lbs. The recommended excitation voltage is 10 volts DC. We will supply the recommended excitation voltage of 10 volts DC.
The output voltage of the load cell with 10 volts excitation will be (10 volts) * (3 millivolts/volt) = 30 millivolts = 0.030 volts. When a load of 200 lbs is on the load cell, it will output 0.030 volts DC. We want to amplify that to 6 volts so we determine the required amplifier gain as follows:
Amplifier Gain = (Desired voltage)/(Load cell output voltage) = (6 volts)/(0.030 volts) = 200 = Gain
The value for the resistor can be found with the following equation:
Resistor (ohms) = (60,000)/(Gain – 4) = (60,000)/(200 – 4) = (60,000)/196 = 306 ohms = Desired resistor value in schematic
It probably is not possible to get a single resistor at 306 ohms. You can just pick the resistor value closest to it and use a 300 ohm resistor. You can also hook multiple resistors in series to obtain the desired resistance. In this case, you could use a 300 ohm resistor connected to a 6 ohm resistor or any combination of resistors to give you 306 ohms.